
Fueling
the
Future
SMART IAC's innovative approach
to decarbonization
By SHARON HENRY

In a groundbreaking achievement, the University of California, Irvine's SMART Industrial Assessment Center (SMART IAC) was recognized for its exceptional research efforts in energy engineering. Recently, the center received a prestigious award of $25,000 from the U.S. Department of Energy's Advanced Manufacturing Office, applauding its excellence in applied energy engineering research. This recognition opens up exciting possibilities for undergraduate and graduate students to embark on energy assessment-inspired research projects.

A Unique Approach
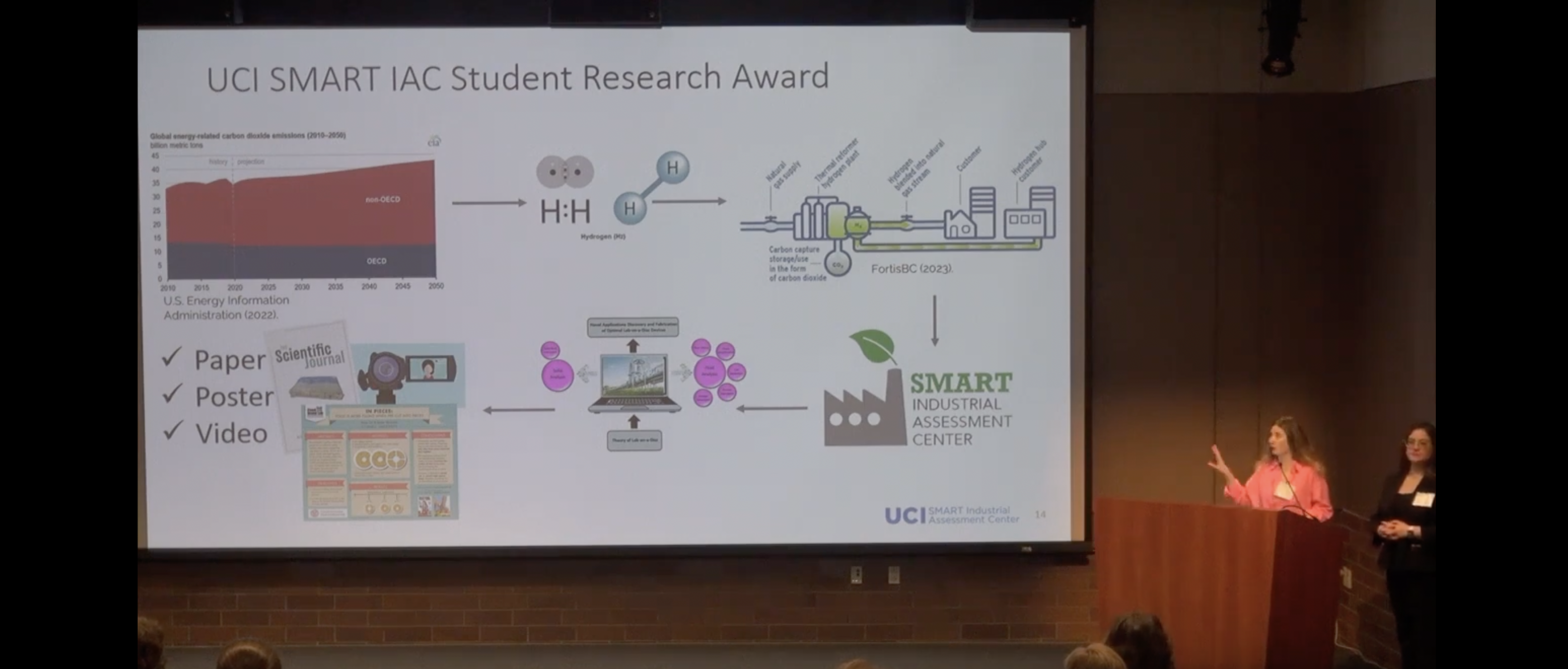
SMART IAC students, along with their team advisor G.P. Li, UCI CALIT2/INRF/SMART IAC director, stood out for their innovative proposal titled, "Mixing Hydrogen with Natural Gas as an Alternative for Fuel Switching in Manufacturing for Decarbonization/Reducing GHG Emission."
“Decarbonization is a hot topic,” said Chelsea Choudhary, SMART IAC program manager. “We chose a related topic but instead of electrification we took a more unique approach. For many reasons electrification might not be an option for decarbonization– financial barriers, process-specific barriers, etc. Our proposal is to switch natural gas processes to using a hydrogen/natural gas blend. While this does not eliminate the use of natural gas, it does reduce it, therefore reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This is a good step toward decarbonization in situations where pure electrification is not feasible.”
When hydrogen is burned, it produces only water vapor as a byproduct, resulting in minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, blending hydrogen with natural gas could significantly lower the overall carbon footprint of the energy supply.
Blending hydrogen into natural gas involves mixing a certain percentage of hydrogen with the traditional natural gas supply in pipelines. This process allows for the co-distribution of both gases, enabling consumers to receive a blended fuel mixture.
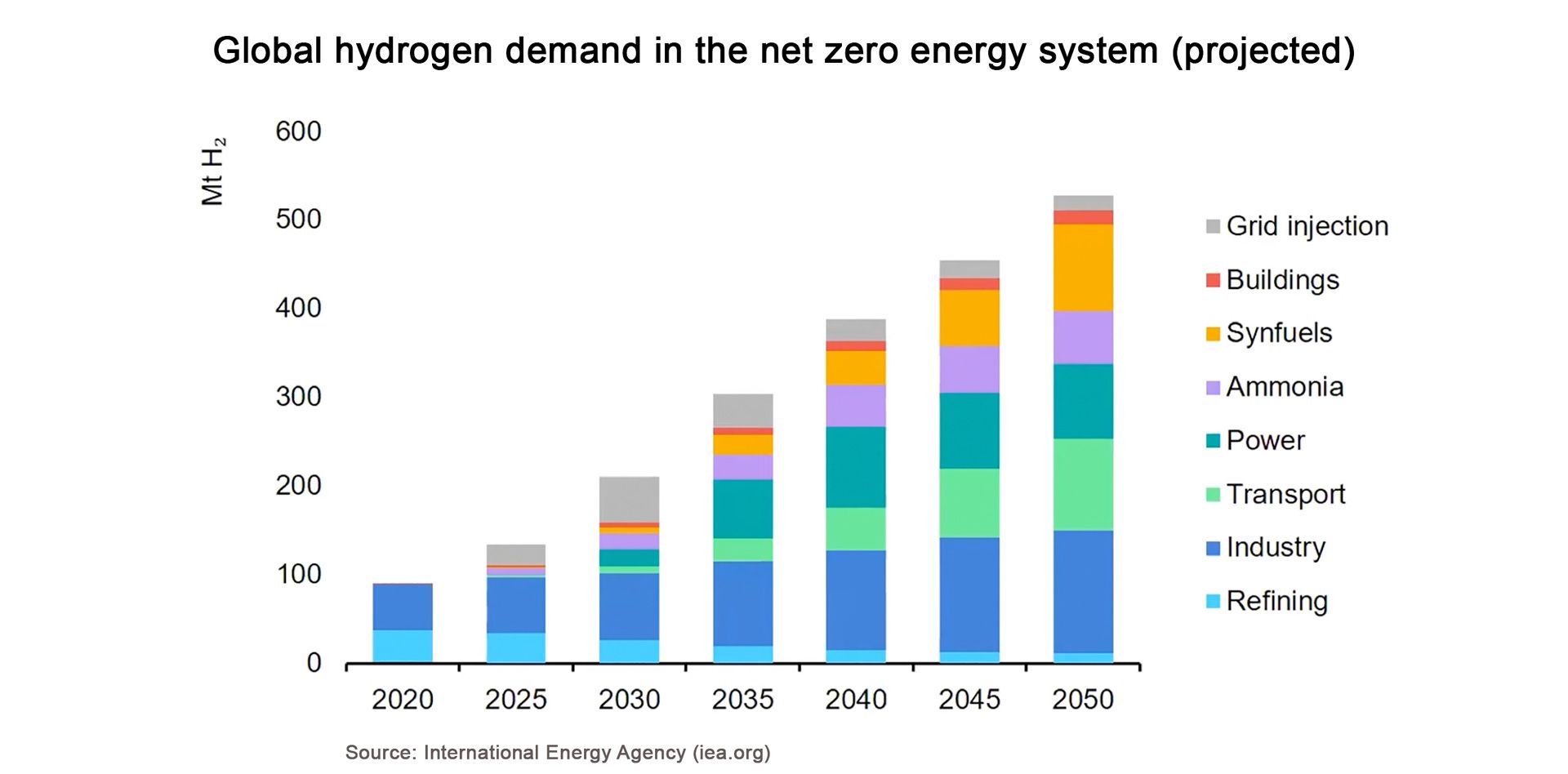
Hydrogen, a high-energy molecule with no CO2 emissions when consumed, holds enormous potential as a sustainable fuel. The International Energy Agency (IEA) views hydrogen as one of the most promising opportunities to achieve global net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050, a crucial target to address climate change effectively.
The Biden administration has set ambitious carbon reduction targets, aiming for a 50 percent reduction in economy-wide net greenhouse gas pollution by 2030 and achieving a 100 percent carbon pollution-free electricity sector no later than 2035.
The ultimate goal is to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. These targets align with the Paris Agreement, which was ratified by most developed nations worldwide.
The Cost Factor

One significant obstacle in widespread adoption of low-carbon hydrogen is the production cost. Currently, producing hydrogen from renewable sources costs around $5 per kilogram in the U.S., primarily driven by expenses associated with acquiring and installing renewable power equipment, electrolyzers and hydrogen compressors. However, the DOE aims to unlock new markets for hydrogen and achieve an 80 percent cost reduction.
Technological advances and economies of scale offer hope for reducing costs further. The IEA's Roadmap to Net Zero by 2050 envisions a scenario where hydrogen from renewables could cost as little as $1.30 per kilogram by 2030 in regions with abundant renewable resources. This makes clean hydrogen from solar photovoltaic ("PV") electricity cost-competitive with hydrogen from natural gas.
The Road Ahead

The U.S. is at a pivotal moment in its journey toward decarbonization. Hydrogen is set to play a vital role as a clean fuel in the future of major U.S. industrial sectors. To meet the ambitious targets set by the Biden administration, collaboration between regulators and industry participants is crucial to incentivize the development of large-scale, clean hydrogen projects. Challenges may lie ahead, but the potential benefits of pioneering these sustainable energy solutions far outweigh the consequences of maintaining the status quo. Market participants are encouraged to seize the first-mover advantage and become champions of a cleaner, greener future.
Hydrogen Edition
In accordance with the regulations established by the Department of Energy, Industrial Assessment Centers (IACs) are required to create informative videos that highlight their contributions.
Adhering to this mandate, SMART IAC recently produced a visual presentation titled "The Hydrogen Revolution," effectively conveying the vast potential of hydrogen as a sustainable fuel source.
SMART IAC OVERVIEW
In 2021, UC Irvine received nearly $2.25 million of a $60 million investment by the U.S. Department of Energy to assist small- and medium-sized manufacturers in reducing their greenhouse gas emissions and lowering energy costs, while training the next generation of energy-efficiency workers.
The Sustainable Manufacturing Alliance for Research and Training Industrial Assessment Center (SMART IAC), housed at UCI’s California Institute for Telecommunications and Information Technology (CALIT2), operates the center with two satellite centers at CSUN and Cypress College. IACs provide small- and medium-sized manufacturers with assessments and recommendations on energy efficiency, productivity improvement, sustainability and competitiveness as well as measure the impacts of these recommendations on reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
“While large, sophisticated companies like SpaceX dominate the public’s perception of manufacturing in Southern California, it is the manufacturers with fewer than 50 employees that produce most of the innovation, output and employment,” said G.P. Li, project PI and UCI CALIT2 director. “I am proud that UCI has been selected to help small- and medium-sized manufacturers across America lower their energy costs and reduce greenhouse gas emissions while remaining globally competitive. This is further acknowledgment of UCI’s commitment to clean energy. By harnessing the talent of our brightest minds, we can take on the energy, environmental and economic challenges of tomorrow.
ABOUT US
Our SMART IAC provides no-cost energy consulting services to small- and medium-sized manufacturers within 150 miles of UC Irvine (Orange, Ventura, Imperial and Riverside counties.) We have expanded our program to provide commercial building assessments, too.
Our assessments typically require one day on site in your facility and we typically identify 10-20% energy and productivity savings.
As part of our services, we will deliver a detailed, professional report outlining several ways that your facility can save energy and money. Our analysis includes detailed engineering and economic calculation of potential energy saving ideas. We typically only target recommendations that result in a 2-year financial payback for our clients.
__________________________
UC IRVINE CALIT2

featuring the SMART IAC
__________________________
Credits
Writer: Sharon Henry
Video: Natalie Tso
Editor: Shelly Nazarenus
